DOLPH NEWS
Dolph Microwave Designs And Manufactures For Precision Waveguide Components, Earth Station Antennas And Sub-Assemblies For Wireless, Satellite, Aerospace, Defence And Scientific Research
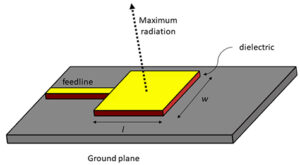
Passive Antenna Advantages | 5 Key Benefits
Zero Maintenance Needs Passive antennas sidestep nearly all maintenance headaches because they contain no electronics or moving parts. Unlike active antennas – which require quarterly
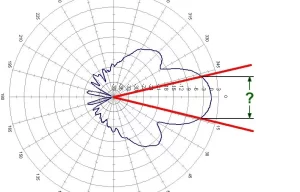
Key Antenna Parameters | 6 Metrics to Track
When designing or selecting an antenna, tracking six key parameters ensures optimal performance. The gain, typically ranging from 3 dBi to 20 dBi, determines directional
Improving Antenna Efficiency | 5 Proven Methods
Improving antenna efficiency involves optimizing design and materials. Use high-conductivity metals like copper (5.8×10⁷ S/m) to reduce resistive losses. Minimize dielectric losses with low-loss substrates

Antenna Power Divider Guide | 6 Uses Explained
An antenna power divider splits RF signals evenly or unevenly across multiple outputs, crucial for applications like multi-antenna systems, signal distribution, and phased arrays. For
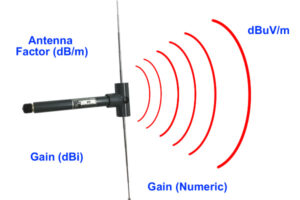
How to Choose High Gain Antenna | 4 Factors
Selecting a high-gain antenna requires evaluating four key factors: frequency range (e.g., 2.4GHz or 5GHz for Wi-Fi), gain rating (15-20dBi for long-range), radiation pattern (omnidirectional

High Gain Horn Antenna Performance | 7 Metrics
High gain horn antennas excel in performance with key metrics: gain (15-25 dBi), frequency range (1-40 GHz), and VSWR (<1.5:1). They achieve 90% radiation efficiency

Setting Up Antenna Controller in 4 Easy Steps
To install an antenna controller, first mount the unit within 3 ft of the antenna using waterproof housing if outdoors. Next, connect the control cables

Antenna Couplers Explained | 3 Core Benefits
Antenna couplers dynamically match your radio’s impedance (typically 50Ω) to an antenna’s fluctuating impedance—preventing up to 70% power waste as heat or reflected energy. For

Optimizing Antenna Feeder System with 5 Pro Tips
A poorly optimized feeder system can waste up to 30% of transmitted power due to mismatches and losses. Start by keeping VSWR below 1.5:1—every 0.1

Passive vs Active Antennas: 4 Crucial Differences
Passive antennas, which rely solely on external signal strength, typically deliver gains between 2 dBi and 10 dBi, making them ideal for short-range, low-interference environments.

What is Antenna Feedhorn | 3 Key Applications
An antenna feedhorn is a crucial component in RF and microwave systems, directing signals between the antenna and receiver/transmitter. Used in 80% of satellite dishes
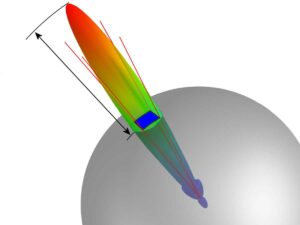
How to Measure Antenna Gain in 5 Simple Steps
Measuring antenna gain accurately is crucial for optimizing wireless performance. Studies show that a 3dB gain improvement can double signal range in ideal conditions. Whether

Waveguide Suppliers Comparison | 5 Essential Metrics
Five key indicators for comparing waveguide suppliers: 1) frequency range (such as 26.5–40 GHz); 2) insertion loss (≤0.2 dB/m); 3) standing wave ratio (VSWR≤1.2); 4)

Waveguide Installation Guide | 5 Step by Step Procedures
The five-step process for waveguide installation is as follows: 1) Check the flatness of the flange surface (<0.05mm); 2) Clean the contact surface and apply
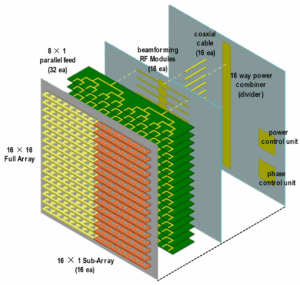
Phased Array Antenna Design | 4 Cost-Saving Techniques
Four cost-reduction technologies for phased array antenna design: 1) Use a multi-layer PCB integrated feed network to reduce interconnect components; 2) Use low-cost LCP materials

Phased Array Antenna Manufacturers | 6 Selection Criteria
Six major criteria for selecting phased array antenna manufacturers: 1) frequency coverage (e.g. 2–40 GHz); 2) gain accuracy (within ±1 dB); 3) beam switching speed

Waveguide vs Coaxial Cable | 3 Performance Differences
There are three major performance differences between waveguide and coaxial cable: 1) Frequency range: waveguide is suitable for high frequency bands above 30GHz, while coaxial

How to Test Waveguide Assemblies | 3 Effective Methods
Three effective methods for testing waveguide components include: 1) using a vector network analyzer (VNA) to measure S parameters, ensuring that the frequency range covers
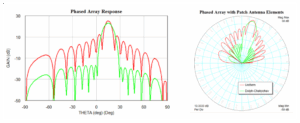
Phased Array Antenna vs Traditional | 4 Key Benefits
Phased array antennas have four major advantages over traditional antennas: 1. Fast beam scanning speed, up to microseconds; 2. Multi-beam capability, supporting simultaneous multi-target tracking;

Waveguide vs Microstrip | 3 Design Considerations
Design considerations for waveguide and microstrip lines: 1. Loss: waveguide loss is less than 0.05dB/m, while microstrip loss is about 0.5dB/m. 2. Frequency response: waveguide

How to Select Waveguide Manufacturers | 5 Key Factors
Five key factors for selecting a waveguide manufacturer: 1. Precision, ensure tolerance ≤ 0.02mm; 2. Material quality, preferably high conductive alloys; 3. Cost-effectiveness, compare quotations,



