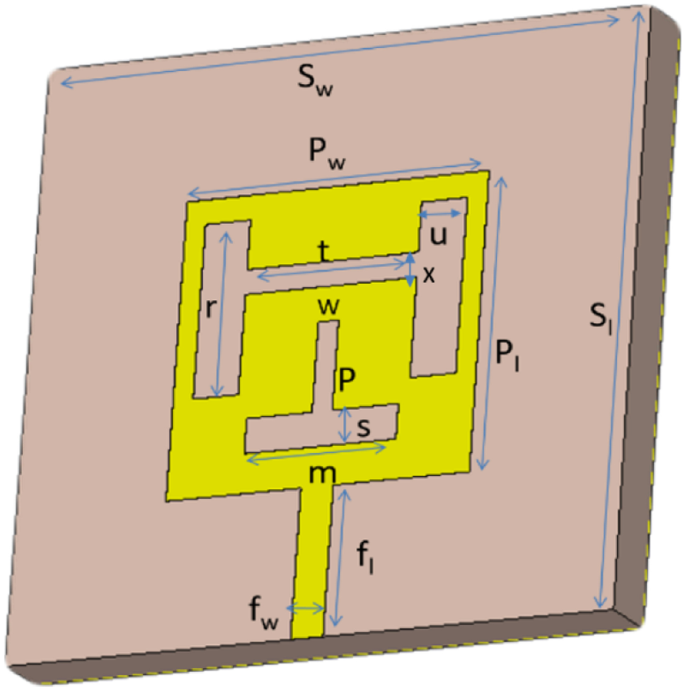
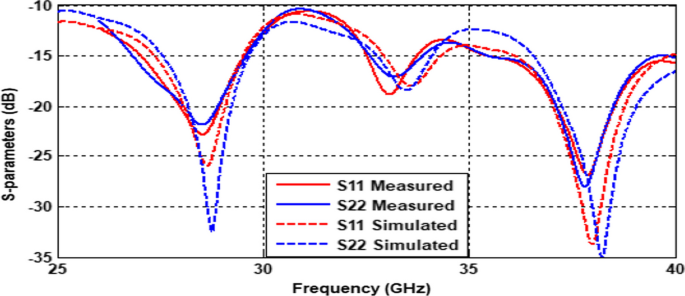
Waveguide vs coaxial cable for antennas | which is better
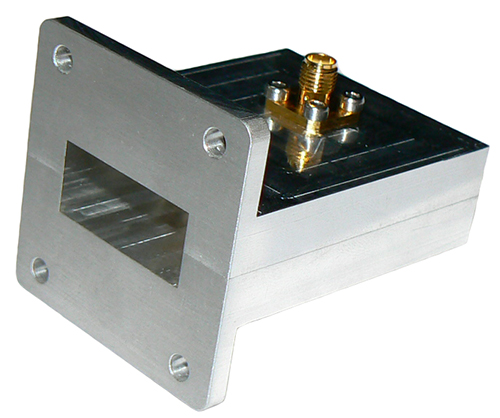
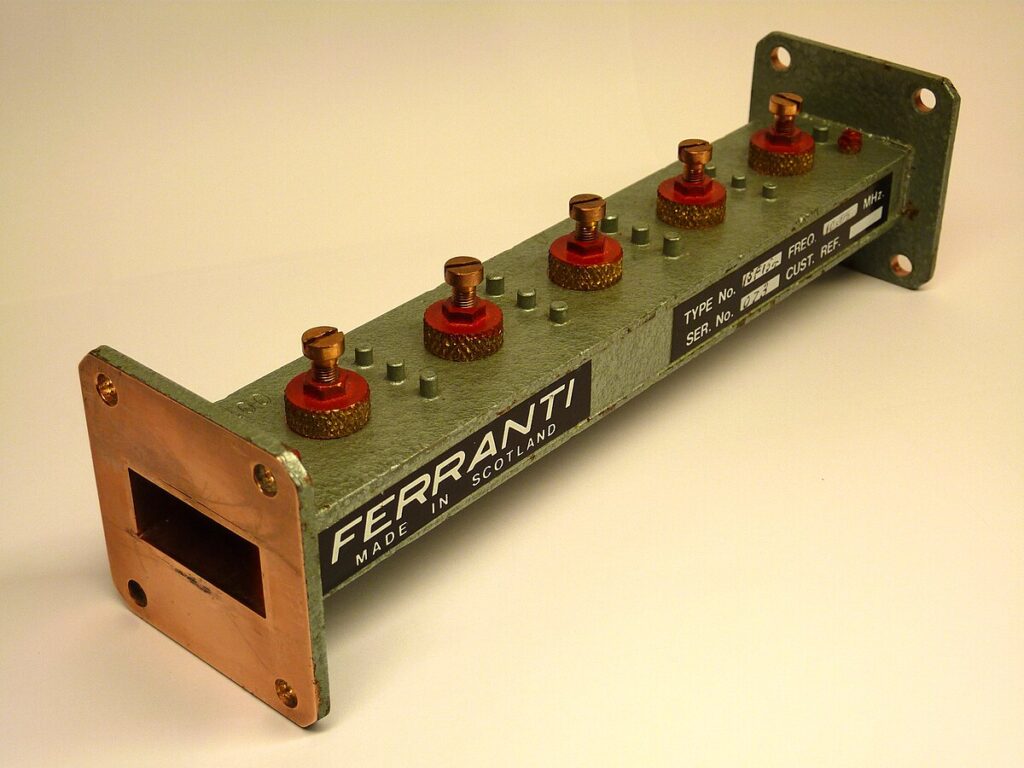
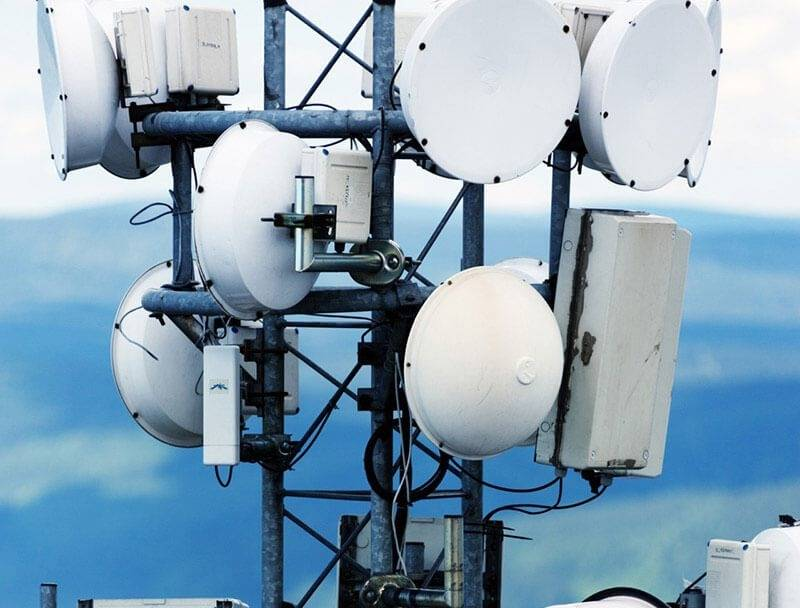
Waveguides outperform coaxial cables for high-frequency (5GHz+) antenna systems, offering lower signal loss (0.1dB/m vs 0.5dB/m in RG-8U at 10GHz) and higher power handling (kW range vs 300W for 1-5/8″ coax). Their rigid aluminum construction minimizes EMI interference, though requiring precise flange connections (WR-90 standard for X-band) versus coax’s flexible F-connector installations. Choose waveguides for […]
Waveguide vs coaxial cable for antennas | which is better Read More »