What Is a Waveguide Choke Flange Design
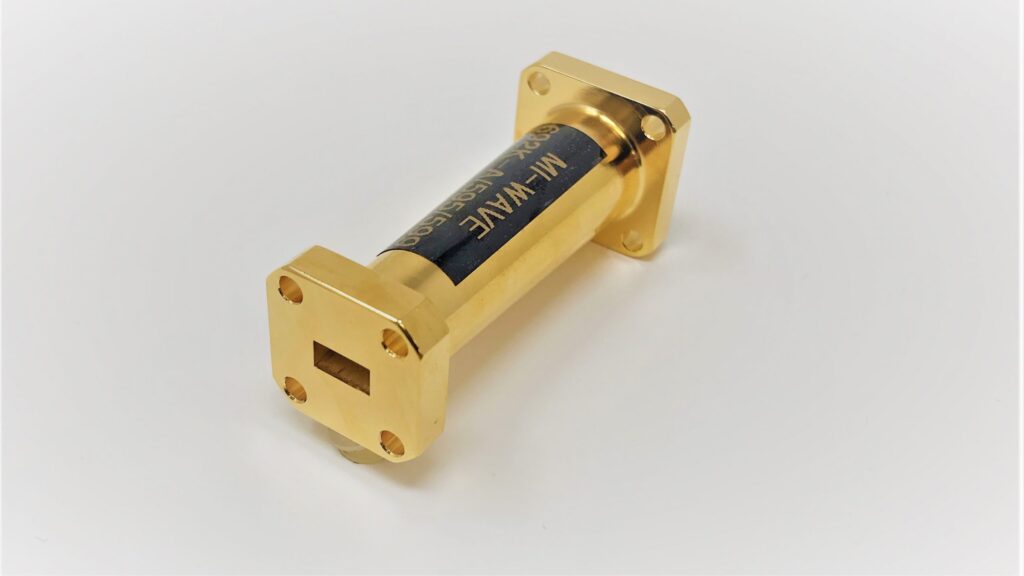
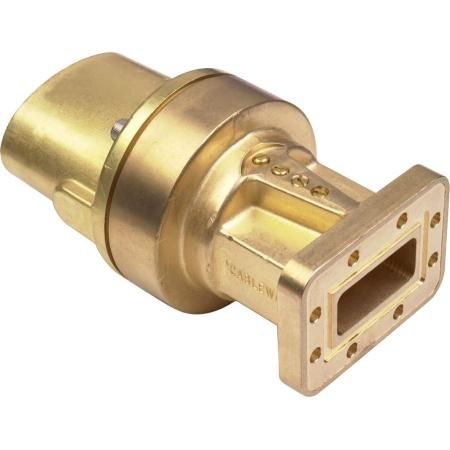
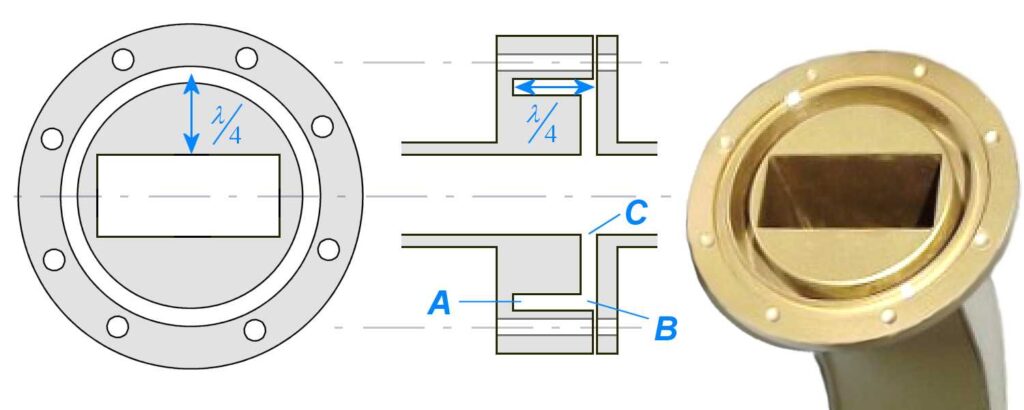
A choke flange suppresses RF leakage via a λ/4-deep groove (e.g., 7.5 mm for 10 GHz) around the mating surface. It uses annular slots to reflect waves, achieving >30 dB return loss. Must maintain 0.05 mm flatness tolerance (per MIL-F-3922) and gold-plated contacts for low resistance (<0.1Ω). Common in radar/WiGig systems. Flange Structure At 3 […]
What Is a Waveguide Choke Flange Design Read More »